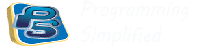To understand the linear search, let's assume you have a friend who lives on a street containing 20 houses. But you forgot the house number, so how do you find the house number where your friend lives? We will assume that the only way to find out is to visit the house and ask if your friend lives there. Please note that you can't ask anyone directly about your friend's house number. So you visit the first house and ask if your friend lives there? If the answer is no, you visit the second one or stop if the answer is yes. You repeat this till you find the house in which your friend lives. This is how linear search works. Now let's see how it works in computers.
Linear search in C to find whether a number is present in an array. If it's present, then at what location does it occur? It is also known as a sequential search. It is straightforward and works as follows: we compare each element with the element to search until we find it or the list ends. Linear search for multiple occurrences and using a function.
Linear search program in C
int main()
{
int array[100], search, c, n;
printf("Enter number of elements in array\n");
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("Enter %d integer(s)\n", n);
for (c = 0; c < n; c++)
scanf("%d", &array[c]);
printf("Enter a number to search\n");
scanf("%d", &search);
for (c = 0; c < n; c++)
{
if (array[c] == search) /* If required element is found */
{
printf("%d is present at location %d.\n", search, c+1);
break;
}
}
if (c == n)
printf("%d isn't present in the array.\n", search);
return 0;
}
Output of program: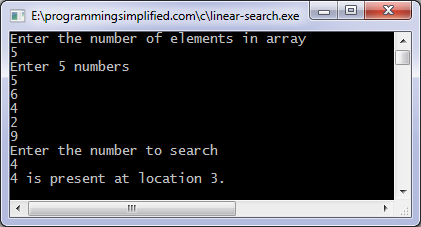
Download Linear search program.
C program to search a character in a string using linear search
int main()
{
char s[1000], x;
int n = 0;
printf("Enter a string\n");
gets(s);
printf("Enter a character to search\n");
scanf("%c", &x);
while (s[n] != '\0') {
if (s[n] == x) {
printf("%c is present at location %d in the string\n", x, n+1);
break;
}
n++;
}
if (s[n] == '\0')
printf("%c is not present in the string\n", x);
return 0;
}
Linear search C program for multiple occurrences
In the code below, we will print all locations at which the required element is found and also the number of times it occurs in the list.
int main()
{
int array[100], search, c, n, count = 0;
printf("Enter number of elements in array\n");
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("Enter %d numbers\n", n);
for (c = 0; c < n; c++)
scanf("%d", &array[c]);
printf("Enter a number to search\n");
scanf("%d", &search);
for (c = 0; c < n; c++) {
if (array[c] == search) {
printf("%d is present at location %d.\n", search, c+1);
count++;
}
}
if (count == 0)
printf("%d isn't present in the array.\n", search);
else
printf("%d is present %d times in the array.\n", search, count);
return 0;
}
Download Linear search multiple occurrence program.
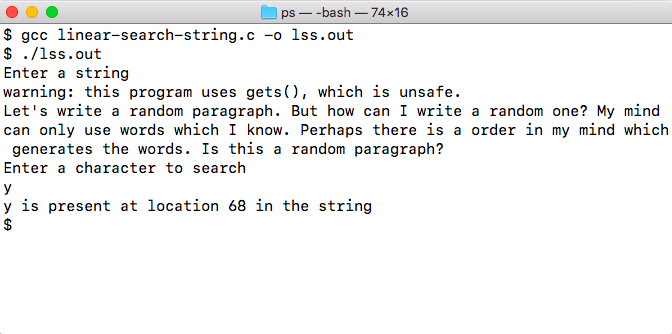
Output of code: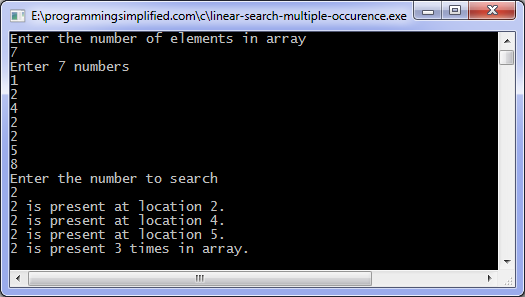
C program for linear search using a function
long linear_search(long [], long, long);
int main()
{
long array[100], search, c, n, position;
printf("Input number of elements in array\n");
scanf("%ld", &n);
printf("Input %d numbers\n", n);
for (c = 0; c < n; c++)
scanf("%ld", &array[c]);
printf("Input a number to search\n");
scanf("%ld", &search);
position = linear_search(array, n, search);
if (position == -1)
printf("%d isn't present in the array.\n", search);
else
printf("%d is present at location %d.\n", search, position+1);
return 0;
}
long linear_search(long a[], long n, long find) {
long c;
for (c = 0 ;c < n ; c++ ) {
if (a[c] == find)
return c;
}
return -1;
}
Linear search function using pointers
long c;
for (c = 0; c < n; c++) {
if (*(p+c) == find)
return c;
}
return -1;
}
The time required to search for an element using the algorithm depends on the size of the list. In the best case, the element is present at the beginning of the list, and in the worst case, it is present at the end. Its time complexity is O(n).