C program to check whether a character is a vowel or consonant: A user inputs a character, and we check whether it's a vowel. Both lower-case and upper-case are checked.
If a character isn't a vowel, it isn't necessarily a consonant, because it might be a digit or a special symbol.
Check vowel using if else
int main()
{
char ch;
printf("Enter a character\n");
scanf("%c", &ch);
// Checking both lower and upper case, || is the OR operator
if (ch == 'a' || ch == 'A' || ch == 'e' || ch == 'E' || ch == 'i' || ch == 'I' || ch =='o' || ch=='O' || ch == 'u' || ch == 'U')
printf("%c is a vowel.\n", ch);
else
printf("%c isn't a vowel.\n", ch);
return 0;
}
C program to check vowel or consonant using if else
In this program, we check whether a character is a vowel, a consonant, a punctuation, or a symbol.
int main()
{
char ch;
printf("Input a character\n");
scanf("%c", &ch);
if ((ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') || (ch >= 'A' &&ch <= 'Z')) {
if (ch=='a' || ch=='A' || ch=='e' || ch=='E' || ch=='i' || ch=='I' || ch=='o' || ch=='O' || ch== 'u' || ch=='U')
printf("%c is a vowel.\n", ch);
else
printf("%c is a consonant.\n", ch);
}
else
printf("%c is neither a vowel nor a consonant.\n", ch);
return 0;
}
Output of the program: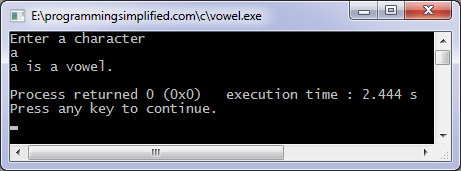
Check vowel using switch statement
int main()
{
char ch;
printf("Input a character\n");
scanf("%c", &ch);
switch(ch)
{
case 'a':
case 'A':
case 'e':
case 'E':
case 'i':
case 'I':
case 'o':
case 'O':
case 'u':
case 'U':
printf("%c is a vowel.\n", ch);
break;
default:
printf("%c isn't a vowel.\n", ch);
}
return 0;
}
Function to check vowel
{
if (a == 'A' || a == 'E' || a == 'I' || a == 'O' || a == 'U')
return 1;
else if (a == 'a' || a == 'e' || a == 'i' || a == 'o' || a == 'u')
return 1;
else // You may omit this else as the control comes here if the character is not a vowel.
return 0;
}
You can check if a character is a consonant using this function. If it's not a vowel, then it is a consonant, but make sure that it's an alphabet, not a special character.