Armstrong number C program to check whether a number is an Armstrong number or not, it's a number that is equal to the sum of digits raise to the power total number of digits in the number. Some Armstrong numbers are: 0, 1, 2, 3, 153, 370, 407, 1634, 8208, etc. Read more about Armstrong numbers. We will consider base ten numbers in our program. The algorithm to do this is: First, we calculate the number of digits in our program and then compute the sum of individual digits raise to the power number of digits. If this sum equals the input number, then the number is an Armstrong number otherwise not. C program to print Armstrong numbers
Examples:
7 = 7^1
371 = 3^3 + 7^3 + 1^3 (27 + 343 +1)
8208 = 8^4 + 2^4 +0^4 + 8^4 (4096 + 16 + 0 + 4096).
1741725 = 1^7 + 7^7 + 4^7 + 1^7 + 7^7 + 2^7 +5^7 (1 + 823543 + 16384 + 1 + 823543 +128 + 78125)
Armstrong number program in C
int power(int, int);
int main()
{
int n, sum = 0, t, remainder, digits = 0;
printf("Input an integer\n");
scanf("%d", &n);
t = n;
// Count number of digits
while (t != 0) {
digits++;
t = t/10;
}
t = n;
while (t != 0) {
remainder = t%10;
sum = sum + power(remainder, digits);
t = t/10;
}
if (n == sum)
printf("%d is an Armstrong number.\n", n);
else
printf("%d isn't an Armstrong number.\n", n);
return 0;
}
int power(int n, int r) {
int c, p = 1;
for (c = 1; c <= r; c++)
p = p*n;
return p;
}
Output of program: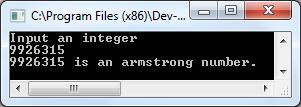
Download Check Armstrong number program.
C program to check Armstrong number using function
We will use long long data type in our program so that we can check numbers up to 2^64-1.
#define L long long
int check_armstrong(L);
L power(int, int);
int main () {
L n;
printf("Input a number\n");
scanf("%lld", &n);
if (check_armstrong(n) == 1)
printf("%lld is an armstrong number.\n", n);
else
printf("%lld isn't an armstrong number.\n", n);
return 0;
}
int check_armstrong(L n) {
L sum = 0, t;
int remainder, digits = 0;
t = n;
while (t != 0) {
digits++;
t = t/10;
}
t = n;
while (t != 0) {
remainder = t%10;
sum = sum + power(remainder, digits);
t = t/10;
}
if (n == sum)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
L power(int n, int r) {
int c;
L p = 1;
for (c = 1; c <= r; c++)
p = p*n;
return p;
}
An output of the program:
35641594208964132
35641594208964132 is an Armstrong number.